Spring Boot 2.x 入门:Spring MVC请求映射(@RequestMapping)入门
一、前言
1、本文主要内容
- Spring MVC简介&工作原理概述
- Spring MVC普通URL映射示例
- Spring MVC带参数URL映射示例
- Spring MVC带HTTP Method约束映射示例
- Spring MVC带HTTP Header约束映射示例
- Spring MVC参数正则约束映射示例
- Spring MVC模糊匹配URL映射示例
2、本教程环境信息
| 软件/环境 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 操作系统 | Windows 10 |
| JDK | 11.0.x |
| Spring Boot | 2.3.0.RELEASE |
| IDE | IntelliJ IDEA 2020 |
| 浏览器 | Chrome 80+ |
3、前置准备
你可能需要的前置知识/准备工作
- MVC框架/模式介绍
https://baike.baidu.com/item/mvc
- 正则表达式
http://www.runoob.com/regexp/regexp-tutorial.html
- 代码
基于 https://ken.io/note/springboot-2.x-helloworld 构建项目
二、Spring MVC简介
Spring MVC是基于Java Servlet构建的MVC架构模式的Web框架,全称是:Spring Web MVC。
- 模型(Model) - 用于封装与应用程序的业务逻辑相关的数据以及对数据的处理方法
- 视图(View) - 用于渲染/呈现数据,通常输出HTML
- 控制器(Controller)- 用于响应用户请求,并将处理后的数据返回或交给对应View来呈现
Spring MVC的核心之一是基于Servlet API封装的DispatcherServlet,每个HTTP请求都需要经过DispatcherServlet来进行分发和处理。
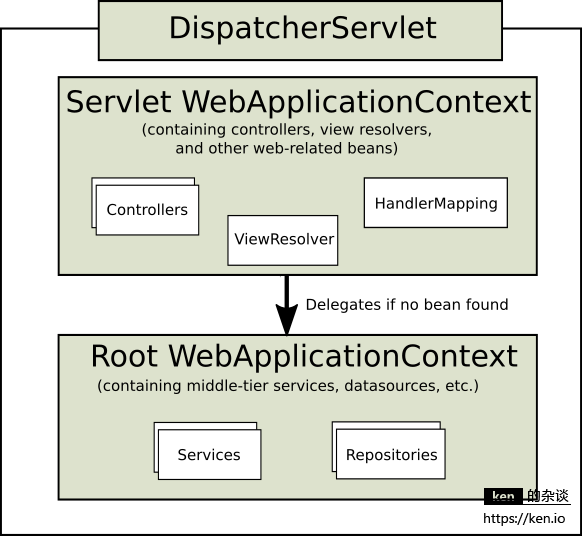
当接收到请求之后,DispatcherServlet会根据HandlerMapping将请求交给Controller去响应和处理,DispatcherServlet会把Controller提供的视图名交给ViewResolver解析到物理视图,并把Controller组装的数据交给视图/模板引擎(JSP/Freemarker等)渲染。
三、请求映射
通常我们会用@RequestMapping注解来配置请求映射。我们可以配置URL、HTTP method、request parameters, headers等属性将请求映射到Controller中对应的方法
1、普通映射
@RequestMapping("/normal")
@Controller
public class NormalMappingController {
@RequestMapping
@ResponseBody
public String normal() {
return "normal normal --ken.io";
}
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
public String normal1() {
return "normal normal1 --ken.io";
}
@RequestMapping(value = {"/a", "/b"})
@ResponseBody
public String normal2() {
return "normal a or b --ken.io";
}
@RequestMapping("/index")
@ResponseBody
public String index() {
return "normal index --ken.io";
}
}
映射说明:
| 控制器Mapping | 方法Mapping | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| @RequestMapping(“/normal”) | @RequestMapping | 匹配URL为/normal的请求 |
| @RequestMapping(“/normal”) | @RequestMapping(“/“) | 匹配URL为/normal/的请求 |
| @RequestMapping(“/normal”) | @RequestMapping(value = {“/a”, “b”}) | 匹配URL为/normal/的请求 |
| @RequestMapping(“/normal”) | @RequestMapping(“/index”) | 匹配URL为/normal/index的请求 |
2、路径参数映射
@RequestMapping("/path")
@Controller
public class PathParamsMappingController {
@RequestMapping("/welcome/{name}")
@ResponseBody
public String name(@PathVariable(name = "name") String name) {
return String.format("path name:%s --ken.io", name);
}
@RequestMapping("/num/{min}/{max}")
@ResponseBody
public String num(@PathVariable(name = "min") Integer min,
@PathVariable(name = "max") Integer max) {
return String.format("path min:%s,max:%s --ken.io", min, max);
}
}
映射说明:
| 控制器Mapping | 方法Mapping | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| @RequestMapping(“/path”) | @RequestMapping(“/welcome/{name}”) | 匹配URL为/path/name/的请求,不包含?/等 |
| @RequestMapping(“/path”) | @RequestMapping(“/num/{min}/{max}”) | 匹配URL为/path/name//的请求,*为数字 |
3、HTTP Method映射
@RequestMapping("/method")
@Controller
public class MethodMappingController {
@PostMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
public String post() {
return "method post --ken.io";
}
@GetMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
public String get() {
return "method get --ken.io";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseBody
public String put() {
return "method put --ken.io";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = {RequestMethod.TRACE, RequestMethod.DELETE})
@ResponseBody
public String other(HttpServletRequest request) {
return "method " + request.getMethod() + " --ken.io";
}
}
映射说明:
| 控制器Mapping | 方法Mapping | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| @RequestMapping(“/method”) | @PostMapping(“/“) | 匹配URL为/method的POST请求 |
| @RequestMapping(“/method”) | @GetMapping(“/“) | 匹配URL为/method的GET请求 |
| @RequestMapping(“/method”) | @RequestMapping(value = “/“, method = RequestMethod.PUT) | 匹配URL为/method的PUT请求 |
| @RequestMapping(“/method”) | @RequestMapping(value = “/“, method = {RequestMethod.TRACE, RequestMethod.DELETE}) | 匹配URL为/method的TRACE、DELETE请求 |
映射测试:HttpMethod=DELETE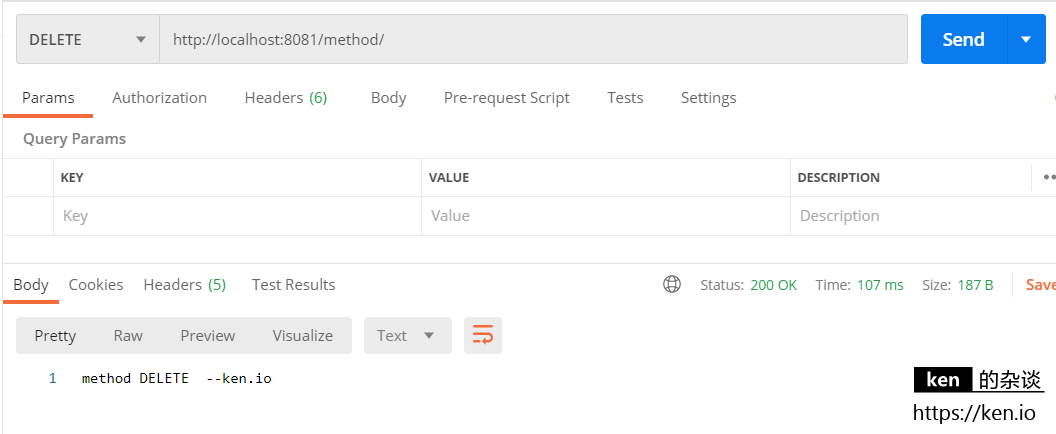
4、HTTP Header映射
@RequestMapping("/header")
@Controller
public class HeaderMappingController {
@RequestMapping(
value = "/",
headers = "type=all"
)
@ResponseBody
public String header() {
return "header type=all --ken.io";
}
@RequestMapping(
value = "/",
produces = "application/json"
)
@ResponseBody
public String produces(HttpServletRequest request) {
return "header produces:application/json --ken.io";
}
}
映射测试:type=all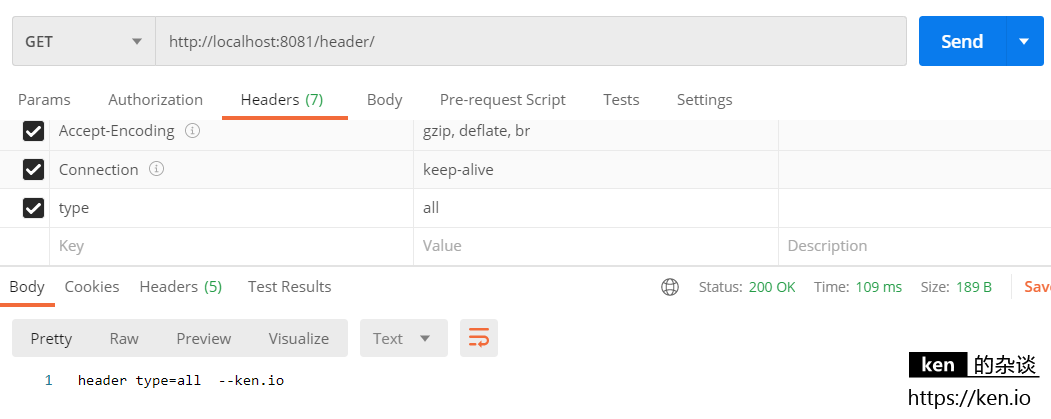
映射测试:Content-Type=application/json
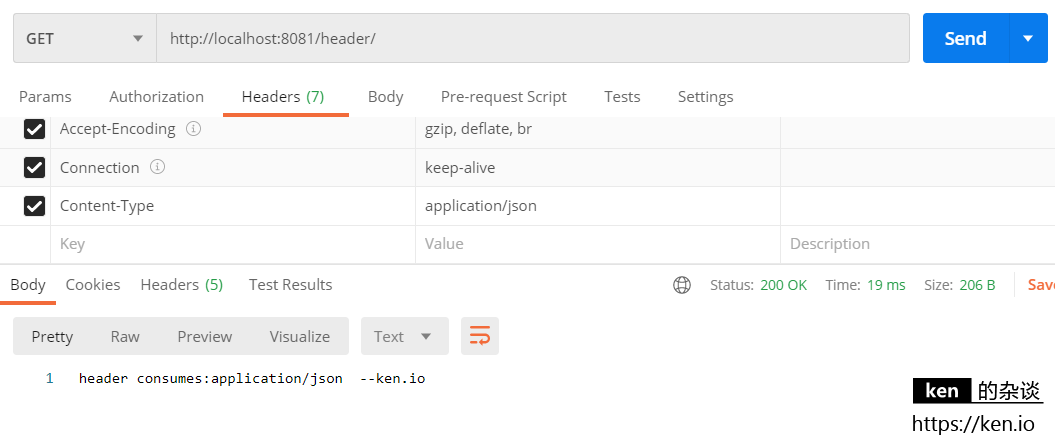
映射测试:Accept=application/json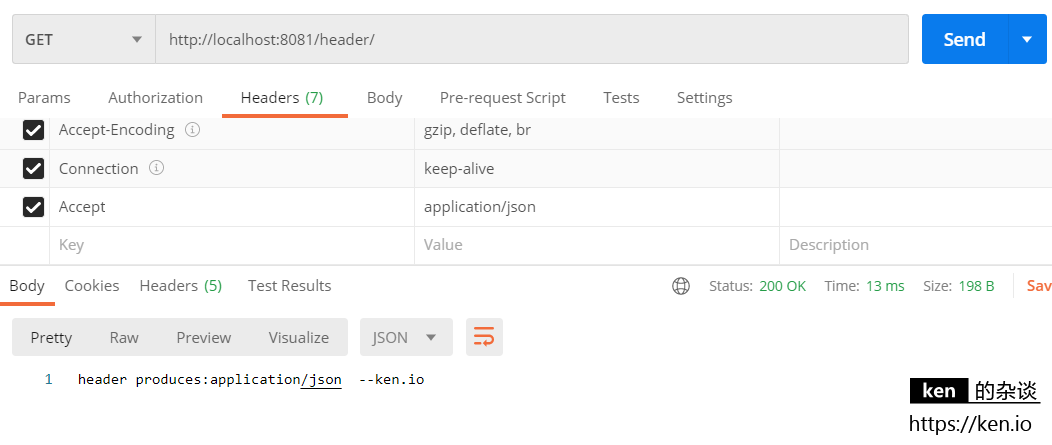
5、通配符映射
@RequestMapping("/fuzzy")
@Controller
public class FuzzyMappingController {
@RequestMapping("/single?")
@ResponseBody
public String single(HttpServletRequest request) {
return "fuzzy single" + request.getRequestURI() + " --ken.io";
}
@RequestMapping("/multi*")
@ResponseBody
public String multi(HttpServletRequest request) {
return "fuzzy multi" + request.getRequestURI() + " --ken.io";
}
@RequestMapping("/regex/{name:[A-z]+}")
@ResponseBody
public String regex(@PathVariable String name, HttpServletRequest request) {
return "fuzzy regex" + name + " , " + request.getRequestURI() + " --ken.io";
}
}
映射说明:
| 控制器Mapping | 方法Mapping | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| @RequestMapping(“/fuzzy”) | @RequestMapping(“/single?”) | 匹配URL为/fuzzy/single?请求,?为1个字符 |
| @RequestMapping(“/fuzzy”) | @RequestMapping(“/multi*”) | 匹配URL为/fuzzy/multi请求,为≥1个字符 |
| @RequestMapping(“/fuzzy”) | @RequestMapping(“/regex/{name:[A-z]+}”) | 匹配URL为/regex/请求,为≥1个英文字母 |
四、备注
1、@RequestMapping注解说明
| 参数 | ken.io的说明 |
|---|---|
| name | 映射名,通常不需要设置 |
| value | 映射地址,可设置一个或多个,默认参数 |
| path | 映射地址,可设置一个或多个,等同于value |
| params | 映射参数,可设置一个或多个,在此处设置的参数为可选参数 |
| method | 映射HTTP Method,可设置一个或者多个,例如:GET、POST、PUT等等 |
| header | 映射HTTP Header,可设置一个或者多个 |
| consumes | 指定请求的内容类型,例如:application/json |
| produces | 指定返回的内容类型,例如:application/json |
2、附录
- 本文代码示例
https://github.com/ken-io/springboot-tutorial-2.x/tree/master/springmvc-requestmapping
